Horizontal directional drilling (HDD) is a drilling method integral to modern construction and utility installation. Known for its efficiency and minimal environmental footprint, HDD, or, as it is sometimes known, directional boring, offers an array of benefits, from installing underground utilities to reducing surface disruption. This exploration will delve into seven key facts about HDD that spotlight its significance and operational nuances.
What is HDD?
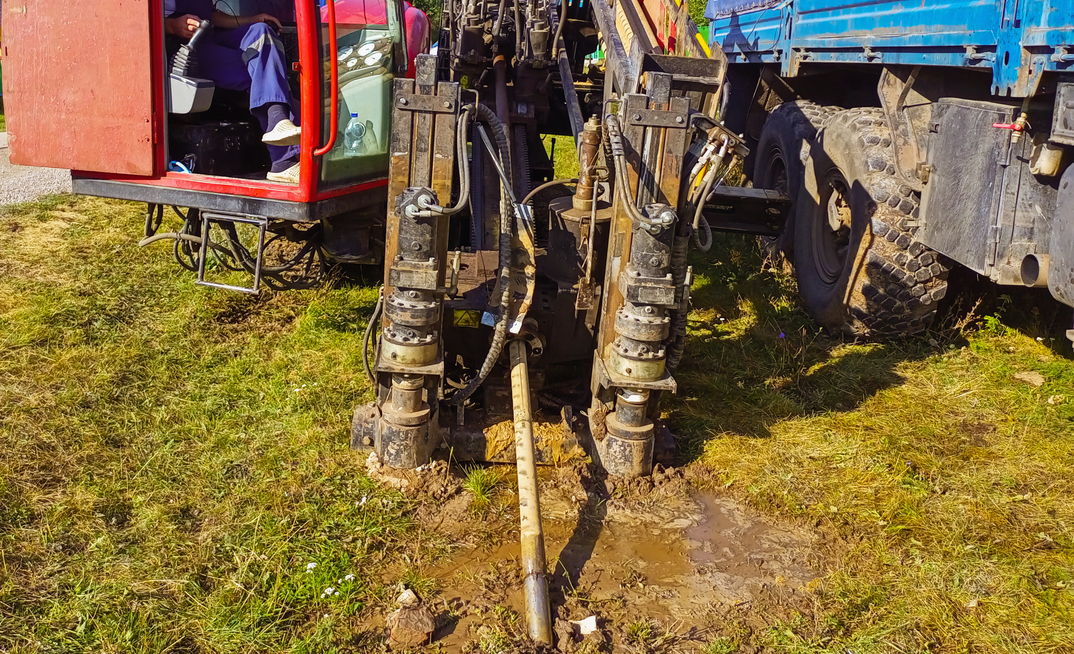
At its core, HDD is a trenchless technology method used to install pipelines, conduits, and cables underground without the need for extensive excavation. This effective method involves drilling a pilot bore path from one surface point to another and then enlarging the hole to accommodate the utility being installed.
Step-by-step
The HDD process can be broken down into three distinct stages:
· Pilot hole drilling: Initially, a small diameter pilot hole is drilled along a predetermined path using a directional drill rig.
· Pre-reaming: Once the pilot hole is completed, it is enlarged in one or more stages to prepare for the installation of the utility pipe.
· Pipe installation: The final step involves pulling the pipe back into the enlarged hole, thus completing the installation process.
The sequential nature of this process ensures precision and minimises the chances of errors during utility installation.
Key equipment
HDD relies on advanced equipment to ensure efficient and accurate drilling. The directional drill rig is the centrepiece, supported by tools like drill bits, reamers, and HDD guidance systems. Additionally, drilling fluids are essential for lubricating the cutting head and stabilising the borehole. These components play crucial roles in the smooth execution of HDD projects.
Environmental impact
One of the most significant advantages of horizontal directional drilling is its reduced environmental impact compared to traditional open-cut methods. HDD disturbs less soil and preserves existing land features and ecosystems. This method is particularly beneficial in sensitive areas, as it diminishes disruption to wildlife habitats and nearby vegetation.
Cost-effectiveness
HDD is not only effective in reducing physical and environmental disruptions but is also cost-efficient over the long term. Though the upfront costs might appear higher (the expense of purchasing a specialist rig, tooling, and staff training), the reduced restoration needs, faster completion times, and lower overall impact can result in significant savings. Additionally, as HDD technology advances, operational efficiencies continue to improve, further driving down directional drilling costs.
Challenges and solutions
Despite its many benefits, HDD does face several challenges, such as steering difficulties in varying soil conditions and potential risks of drilling fluid leakage. However, continuous technological advancements and experienced operators have led to innovative solutions, such as improved drilling fluid systems and advanced navigation technologies, which help mitigate these challenges effectively.
Future trends
The future of HDD looks promising, with ongoing innovations aimed at enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. These include developments in robotic automation, real-time data monitoring, and more environmentally friendly drilling fluids. Such advancements are expected to further solidify HDD's role in modern infrastructure projects, particularly with the increasing demand for fibre-optic installations and renewable energy projects.
Conclusion
HDD stands out as a key technology in the field of construction and utility installation, offering a blend of efficiency, environmental preservation, and cost-effectiveness. From its robust equipment to future technological innovations, the technique continues to evolve, addressing the complex demands of modern-day construction and infrastructure development.
HDD stands out as a key technology in the field of construction and utility installation
As the industry progresses, embracing such trenchless methods in utility installations and infrastructure projects optimises operational demands and aligns with environmental sustainability goals. HDD, without a doubt, plays a pivotal role in shaping the future landscape of construction technology.